Elliptic Curve And It's Applications
- Introduction
- What is Elliptic Curve
- Elliptic Curve's Applications
- Short Weierstrass curves and their representations for fast computations
Introduction
Elliptic curves are a fascinating area of mathematics with profound implications in number theory and cryptography. They provide a rich structure that can be utilized in various applications, particularly in secure communication protocols. In this article, we will explore the fundamental properties of elliptic curves, their group law, and how these mathematical concepts form the basis for several cryptographic algorithms. By understanding elliptic curves, we can gain insight into the underlying principles that ensure the security and efficiency of modern cryptographic systems.
What is Elliptic Curve
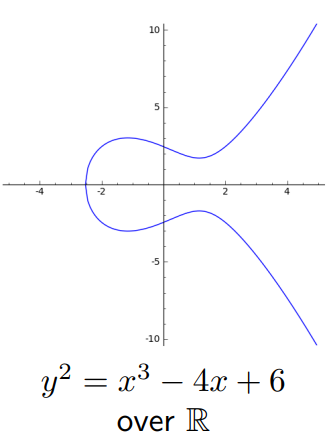
An elliptic curve is the graph of an short Weierstrass equation
where and are constants. Below is an example of such a curve.
The Group Law
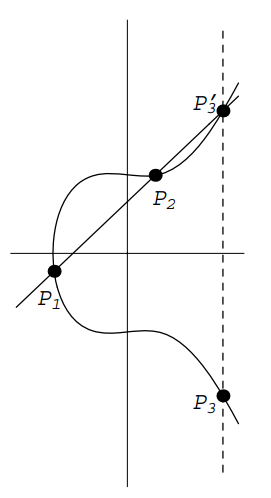
- Adding Points on an Elliptic Curve
Start with two points
on an elliptic curve given by the equation . Define a new point as follows. Draw the line through and . We'll see below that intersects in a third point . Reflect across the axis (i.e., change the sign of the -coordinate) to obtain . We define
Examples below will show that shis is not the same as adding coordinates of the points. It might be better to denote this operation by , but we opt for the simpler notation since we will never be adding points by adding coordinates.
Assume first that and that neither point is . Draw the line through and . Its slope is
If , then is vertical. We'll treat this case later, so let's assume that . The equation of is then
To find the intersection with , substitute to get
This can be rearranged to the form
The three roots of this cubic correspond to the three points of intersection of with . Generally, solving a cubic is not easy, but in the present case we already know two of the roots, namely and , since and are points on both and . Therefore, we could factor the cubic to obtain the third value of x. But there is an easier way. If we have a cubic polynomial with roots , then
Therefore,
If we know two roots , then we can recover the third as .
In our case, we obtain
and
Now, reflect across the axis to obtain the point :
In the case that but , the line through and is a vertical line, which therefore intersects E in . REflecting across the axis yields the same point (this is why we put at both the top and the bottom of the axis).Therefore, in this case .
Now consider the case where When two points on a curve are very close to each other, the line through them approximates a tangent line. Therefore, when the two points coincide, we take the line through them to be the tangent line. Implicit differentiation allows us to find the slope of :
If then the line is vertical and we set , as before. Therefore, assume that . The equation of is
as before. We obtain the cubic equation
This time, we know only one root, namely , but it is a double root since is tangent to at . Therefore, proceeding as before, we obtain
Finally, suppose . The line through and is a vertical line that intersects in the point that is the reflection of across the axis. When we reflect across the axis to get , we are back at . Therefore
for all points on . Of course, we extend this to include .
Let's summarize the above discussion:
Let be an elliptic curve defined by . let and be points on with . Define as follows:
- If , then where .
- If but , then .
- If and , then , where .
- If and , then .
Moreover, define
for all points on .
The addition of points on an elliptic curve satisfies the following properties:
- (Commutativity) for all on .
- (existence of identity) for all points on .
- (existence of inverses) Given on , there exists on with . This point will usually be denoted .
- (associativity) for all on . In other words, the points on form an additive abelian group with as the identity element.
In cryptography, work over instead of . We writh group operation additively . Fix a generator of primer order . In practice, chosen from some standard(e.g. NIST).
Elliptic Curve's Applications
What is discrete logarithm problem
screct , public , recovering from is hard.
ECDSA
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
Schnorr protocol
wants to convince that knows a secret s.t. .
Short Weierstrass curves and their representations for fast computations
http://www.hyperelliptic.org/EFD/g1p/auto-shortw.html